Support it or not, the collection and selling of information has emerged as one of the most lucrative industries of the 21st century, accompanied by a growing violation of personal privacy. Naturally, then, using a secure messaging app has become a growing concern for consumers and businesses alike.
What then makes for a secure messaging app? Let’s take a look at the Electronic Frontier Foundation, the leading non-profit in “defending your rights in the digital realm”, and what they suggest considering before committing to a messaging service.

What does all of this mean? Secure, private messages all the way from sender to receiver, security design open to public inspection, no way for your contacts to fake their identity, no ability for third parties including the developer and law enforcement to decrypt messages (even the FBI couldn’t crack Apple’s encryption). These are just a few checkmarks to the questions above. For a much more detailed explanation of these points, head over to EFF’s official site.
Now for some real-life case studies. With the above information in mind, we took a look at 4 popular messaging apps and saw how they fared up in terms of user security.
Facebook Messenger
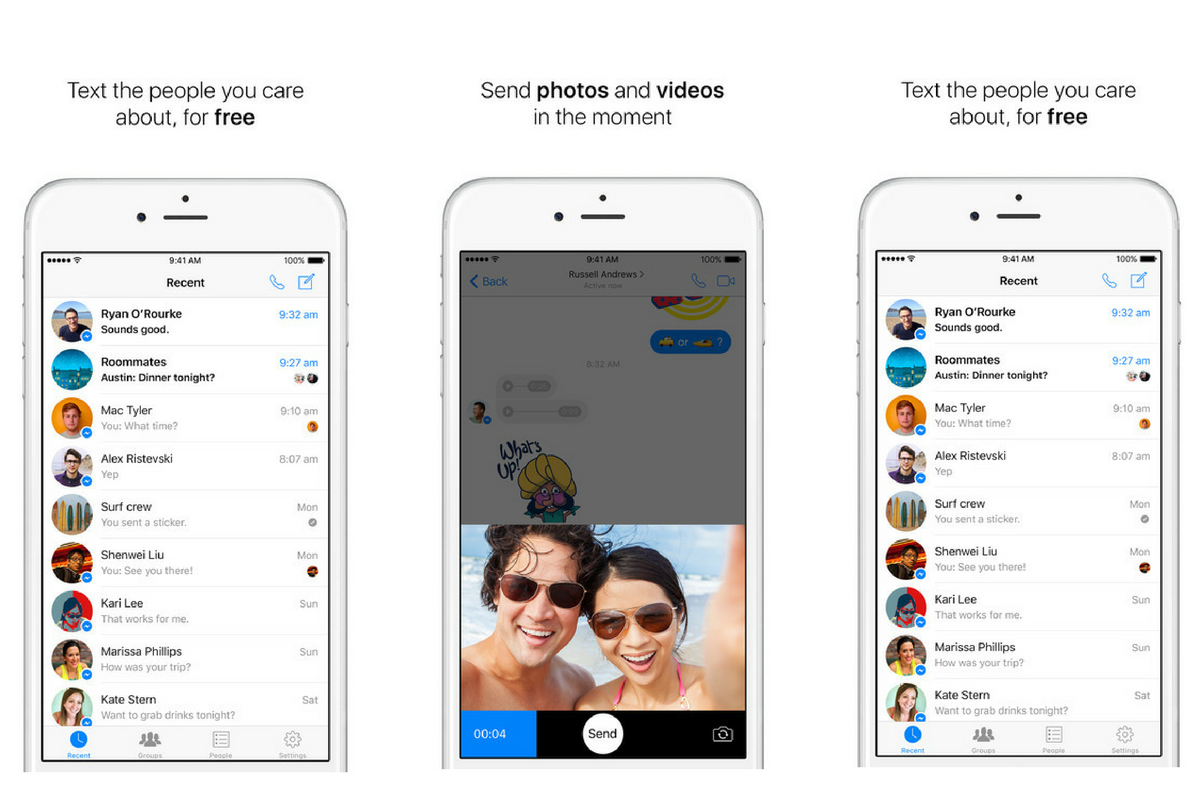
Privacy Features:
Qualifying Facebook Messenger for the upper-echelon of secure messaging is Secret Conversation. Its opt-in, end-to-end encryption (E2EE) feature was introduced this past year. Using the same encryption system as Open Whisper Systems, often considered one of the most secure messaging services on the market, Secret Conversations protects your messages from any potentially intruding third-party.
On top of this E2EE, Secret Conversations also allows users to set timers on their messages–Mission Impossible-style. Users can set timers ranging from five seconds to one day, after which their message is destroyed.
For those who want to go the extra mile and verify that your messages are, in fact, encrypted, sender and receiver can compare device keys–found in Messenger’s “Device Keys” option–to see if they match up.
Things to watch out for:
One downside to Messenger’s Secret Conversations is its annoying opt-in requirement–you must manually turn it on every time you begin a new conversation. Note that only text messages, pictures and stickers are supported in Secret Conversations. Also, Messenger is not open to independent review or open sourced, which means there’s no way to verify that Facebook hasn’t put a backdoor, or that the code doesn’t have vulnerabilities.
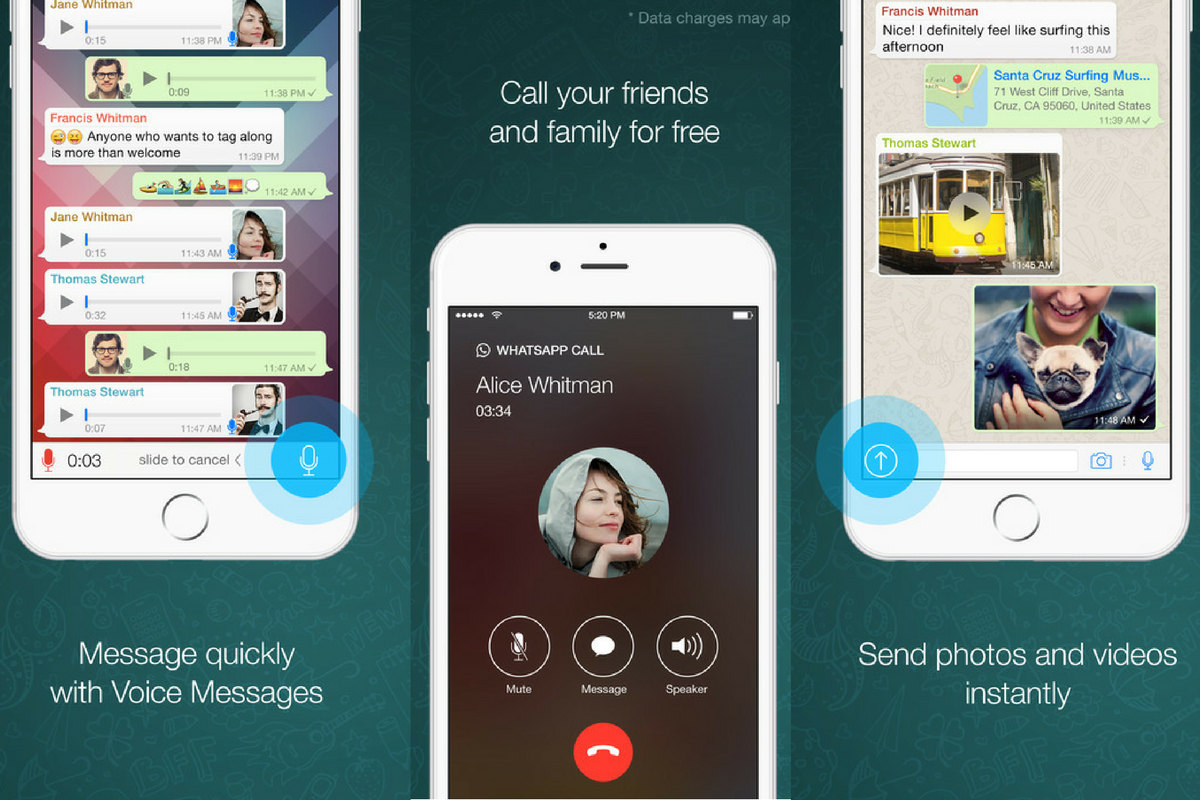
Privacy Features:
Similar to its parent company, Facebook, Whatsapp users can take refuge in the fact that their messages are E2EE. While Whatsapp has proudly boasted encrypted messages as early as 2014, developed in partnership with Open Whisper Systems–the team behind Signal’s esteemed security protocol, it was only in the early months of 2016 that Whatsapp expanded this encryption to include photos, videos, voice messages, documents, and calls.
What’s nice about Whatsapp’s E2EE is that you don’t need to opt-in and there’s no option to opt-out. Every message you send is automatically encrypted. The only thing to make sure here is that both the sender and receiver’s version of Whatsapp is up-to-date, otherwise E2EE might not be guaranteed (the company explains their encryption features).
Things to Watch Out For:
Whatsapp’s greatest potential flaw lies in its ownership. Since 2014, it has been owned by Facebook–a company notorious for user data collection. While it has seemingly stuck to its promise of secure messaging for the most part, an unsettling announcement in September that Whatsapp will begin sharing phone numbers and analytics to Facebook is hard to ignore. It will be interesting to see how Whatsapp balances its obligations in the future. Whatsapp also has the same issues as Messenger: not open sourced and the code has not been independently reviewed.
Telegram
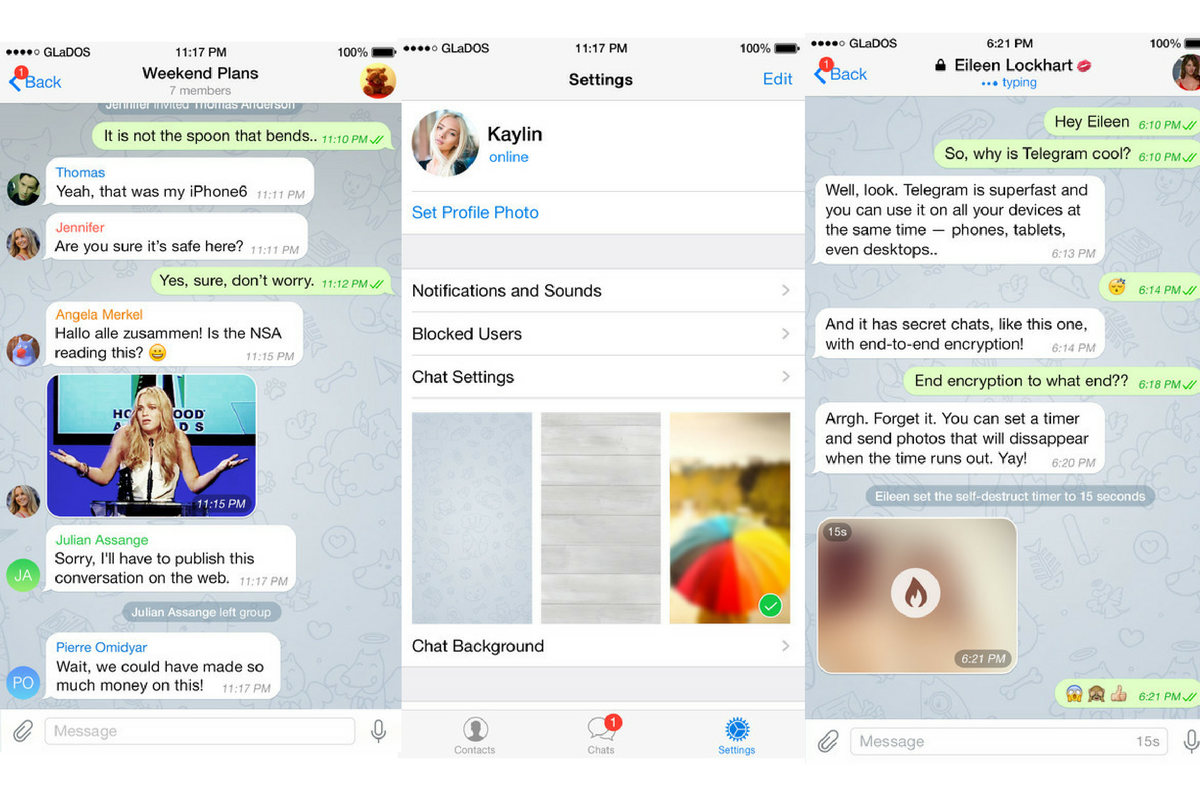
Privacy Features:
Telegram stands out as one of the more customizeable messaging apps. With an open-source API and Bot API, developers can create convenient integrations (like Oursky’s Breakfast bot). As a side note, Facebook recently introduced a not-so-open bot API as well.
Telegram users can opt-in to a secure Secret Chat. Similar to Messenger’s Secret Conversation, Secret Chat provides sender and receiver with secure E2EE.
Other features include device-specific messaging, meaning that messages are not stored in the cloud, meaning that as the sender you can’t view the message unless you are on the device you originally sent it on. If you then delete the message on your device, the receiver will be ordered to delete their copy, and the same goes for messages given a self-destruction timer. Telegram has even gone so far as to offer self-destructing accounts!
Things to watch out for:
Unlike Messenger or Whatsapp, which use the proven Open Whisper Systems-developed encryption protocol, Telegram uses its own form of encryption–a protocol called MTproto, which some believe is not as secure as Signal’s Axolotl (check this discussion). Also, as mentioned above, Telegram’s Secret Chat function is highly secure, but its default chat features act as many other apps, where the messages do not have E2EE, past communications are not secure if keys are stolen, and contact identities are not verified.
Signal by Open Whisper Systems
Privacy Features:
Supported by community donations and grants, Open Whisper Systems does not have pressure to develop a viable business model that often tempts other companies to sell user data. In addition to their flagship messaging app, Signal, Open Whisper Systems has made its Signal protocol public and has contributed to the increased security for apps such as Messenger and Whatsapp. The Signal protocal was developed based on the Off the Record Messaging (ORT) and multiple iterations of the Axolotl Ratchet (renamed as the Double Ratchet Algorithm) and provides confidentiality, integrity, authentication, participant consistency, destination validation, forward and backward secrecy, causality preservation, message unlinkability, message repudiation, participation repudiation, and asynchronicity.
The Signal Protocol also supports E2EE group chats, which also has speaker consistency, out-of-order resilience, dropped message resilience, computational equality, trust equality, subgroup messaging, in addition to the one-to-one features.
For authentication, users can manually compare public key fingerprints through an outside channel to avoid a man-in-the-middle attack.
Things to watch out for:
Even though Open Whisper Systems is open sourced and has admirers like Edward Snowden, security experts recently revealed the Android version had multiple security flaws related to the messaging authentication code (MAC), which could be bypassed. The flaw was fixed in three days after the report was made.
Also, the Signal Protocol does not offer anonymity preservation and requires servers to relay messages and store of public key material.
Which ones qualify as a secure messaging app to EFF?

The good news is that according to EFF’s chart, a handful of chat apps do pass all 7 requirements. They include ChatSecure + Orbot for iOS, Pidgin for Windows desktop, Signal / RedPhone (by Whisper Systems), Silent Circle which includes Silent Phone and even their own Blackphone, Telegram (secret chats) for mobile and web, and TextSecure, which is also by Whispersystems.
There you have it. Armed with an arsenal of seven questions and three real life examples, choosing the most secure messaging service for your specific situation should now hopefully be a little easier.
Of course, these apps are constantly updating, and as we’ve seen with Whatsapp’s latest announcement, keeping up-to-date with the most recent news is probably the best thing you can do to make sure your messages remain as secure as possible.
Have any comments or suggestions surrounding the world of secure messaging? Please throw them down in the comments below!